Chapter 5 Extracting and Visualizing Meteorological Data
“What do you call dangerous precipitation? A rain of terror.”
For this assignment, we used custom functions to read in and look at average meteorological data scraped from a public data archive.
Data is from Snowstudies.org. Assignment by Dr. Matthew Ross and Dr. Nathan Mueller of Colorado State University.
5.1 Extract the meteorological data URLs.
# Read HTML page
snowarchive <- read_html("https://snowstudies.org/archived-data/")
# Read link with specific pattern
links <- snowarchive %>%
html_nodes('a') %>% #look for links
.[grepl('forcing',.)] %>% #filter to only links with "forcing" term
html_attr('href') #tell it these are urls
links # view## [1] "https://snowstudies.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/SBB_SASP_Forcing_Data.txt"
## [2] "https://snowstudies.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/SBB_SBSP_Forcing_Data.txt"5.2 Download the meteorological data from the URL
# Grab only the name of the file by splitting out on forward slashes
splits <- str_split_fixed(links,'/',8)
#Keep only the 8th column
files <- splits[,8]
files## [1] "SBB_SASP_Forcing_Data.txt" "SBB_SBSP_Forcing_Data.txt"# Generate a file list for where the data goes
file_names <- paste0('Data_sci_bookdown/data/snow/', files)
# For loop that downloads each - i for every instance, length function tells how many instances
for(i in 1:length(file_names)){
download.file(links[i],destfile=file_names[i])
}
# Download via map function
#map2(links, file_names, download.file)
# Map version of the for loop (downloading files)
downloaded <- file.exists(file_names)
evaluate <- !all(downloaded) # sees if files are downloaded (T/F)
if(evaluate == T){
map2(links[1:2],file_names[1:2],download.file)
}else{print('data downloaded')}## [1] "data downloaded"5.3 Write a custom function to read in the data and append a site column to the data
# Traditional read in
SASP <- read.csv("Data_sci_bookdown/data/snow/SBB_SASP_Forcing_Data.csv") %>%
select(1,2,3,7,10)
colnames(SASP) <- c("year","month","day","precip","temp")
SBSP <- read.csv("Data_sci_bookdown/data/snow/SBB_SBSP_Forcing_Data.csv") %>%
select(1,2,3,7,10)
colnames(SBSP) <- c("year","month","day","precip","temp")
# Combine csvs
alldata <- rbind(SASP,SBSP)
# Read in via new function
# Grab headers from metadata pdf
library(pdftools)## Using poppler version 20.12.1headers <- pdf_text('https://snowstudies.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Serially-Complete-Metadata-text08.pdf') %>%
readr::read_lines(.) %>%
trimws(.) %>%
str_split_fixed(.,'\\.',2) %>%
.[,2] %>%
.[1:26] %>%
str_trim(side = "left")5.4 Use the map function to read in both meteorological files
# Pull site name out of the file name and read in the .txt files
read_data <- function(file){
name = str_split_fixed(file,'_',2)[,2] %>%
gsub('_Forcing_Data.txt','',.)
df <- read_fwf(file) %>%
select(year=1, month=2, day=3, hour=4, precip=7, air_temp=10) %>% #choose and name columns
mutate(site = name) #add column
}
alldata2 <- map_dfr(file_names,read_data) ## Rows: 69168 Columns: 19
## ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
##
## chr (2): X12, X14
## dbl (17): X1, X2, X3, X4, X5, X6, X7, X8, X9, X10, X11, X13, X15, X16, X17, ...
##
## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
## Rows: 69168 Columns: 19
## ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
##
## chr (2): X12, X14
## dbl (17): X1, X2, X3, X4, X5, X6, X7, X8, X9, X10, X11, X13, X15, X16, X17, ...
##
## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.summary(alldata2)## year month day hour
## Min. :2003 Min. : 1.000 Min. : 1.00 Min. : 0.00
## 1st Qu.:2005 1st Qu.: 3.000 1st Qu.: 8.00 1st Qu.: 5.75
## Median :2007 Median : 6.000 Median :16.00 Median :11.50
## Mean :2007 Mean : 6.472 Mean :15.76 Mean :11.50
## 3rd Qu.:2009 3rd Qu.: 9.000 3rd Qu.:23.00 3rd Qu.:17.25
## Max. :2011 Max. :12.000 Max. :31.00 Max. :23.00
## precip air_temp site
## Min. :0.000e+00 Min. :242.1 Length:138336
## 1st Qu.:0.000e+00 1st Qu.:265.8 Class :character
## Median :0.000e+00 Median :272.6 Mode :character
## Mean :3.838e-05 Mean :272.6
## 3rd Qu.:0.000e+00 3rd Qu.:279.7
## Max. :6.111e-03 Max. :295.85.5 Make a line plot of mean temp by year by site
temp_yearly <- alldata2 %>%
group_by(year, site) %>%
summarise(mean_temp = mean(`air_temp`, na.rm=T))## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'year'. You can override using the `.groups`
## argument.ggplot(temp_yearly,aes(x=year, y=mean_temp, color=site)) +
geom_point() + geom_line() +
xlab("Year") + ylab("Mean Temperature (Degrees Kelvin)") +
ggthemes::theme_few() +
scale_color_brewer(palette = "Set2") +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = pretty(c(2003,2012), n = 6)) +
theme(legend.position="bottom")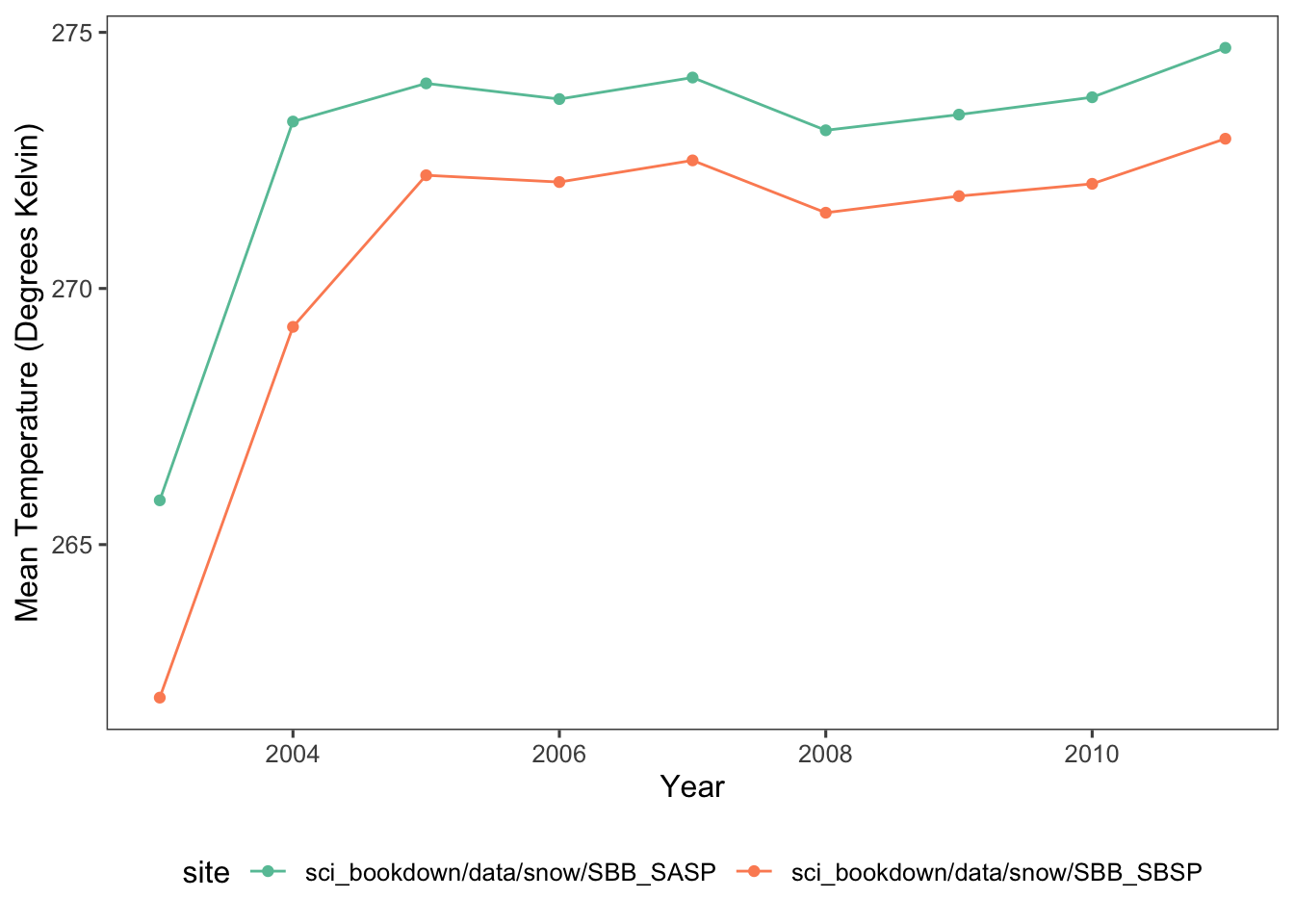
Figure 5.1: Mean temperature of the SASP (teal) and SBSP (orange) sites from 2003 to 2012, in degrees Kelvin.
5.6 Write a function that makes line plots of monthly average temperature at each site for a given year. Use a for loop to make these plots for 2005 to 2010.
temp_monthly <- alldata2 %>%
group_by(year, month, site) %>%
summarize(mean_temp = mean(`air_temp`, na.rm=T))## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'year', 'month'. You can override using the
## `.groups` argument.par(mfrow=c(5,1))
plot_monthly <- function(year.no) {
plot <- temp_monthly %>%
filter(year == year.no) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=month, y=mean_temp, color=site)) +
geom_line() +
xlab("Month") + ylab("Mean Temperature (Degrees Kelvin)") +
ggthemes::theme_few() +
scale_color_brewer(palette = "Set2") +
scale_x_discrete(limits = c(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12)) +
scale_y_continuous(breaks = pretty(c(255,290), n = 4)) +
theme(legend.position="bottom")
print(plot)
}
for(i in 2005:2010){
plot_monthly(i)
}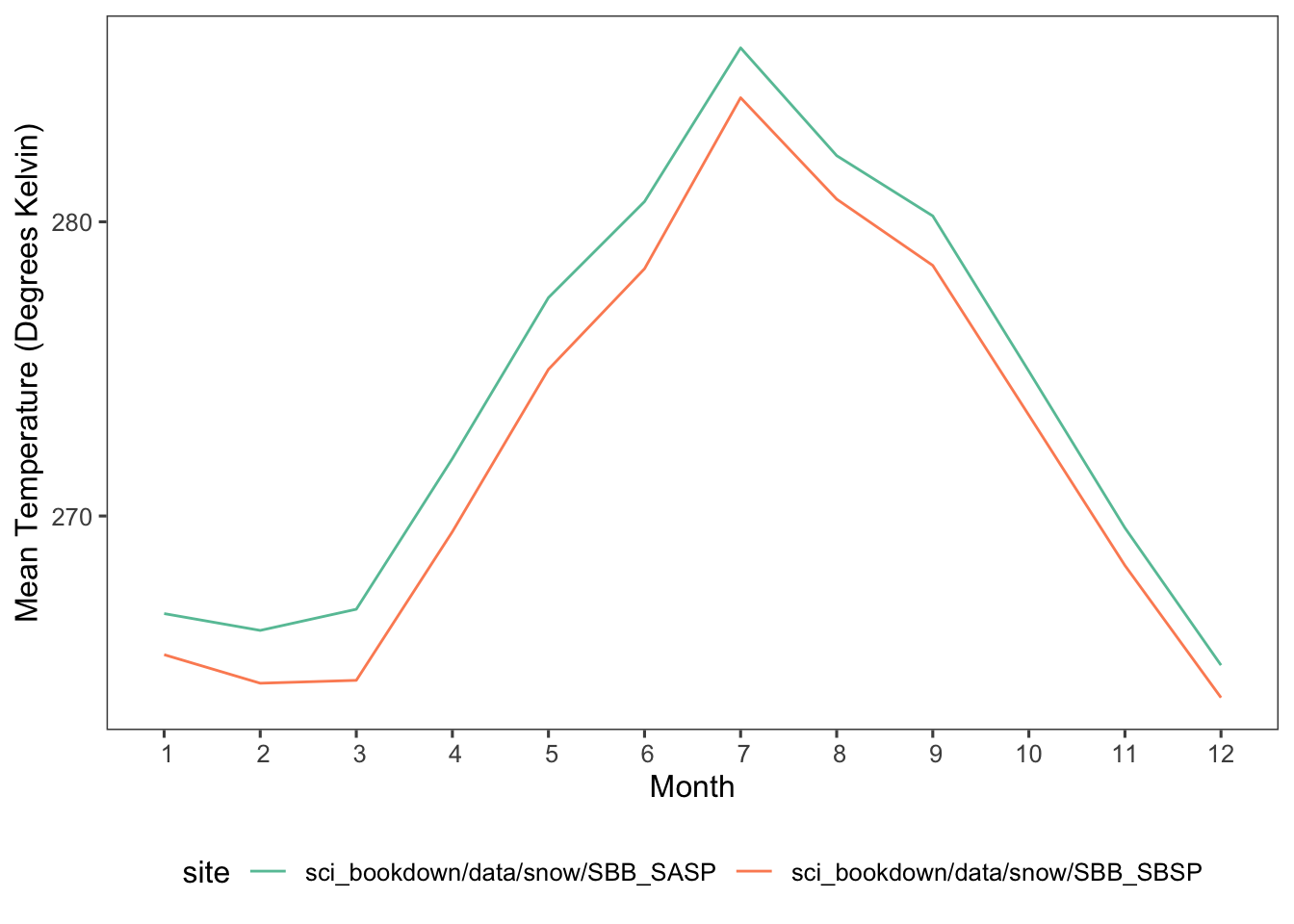
Figure 5.2: Mean monthly temperatures in degrees Kelvin for SASP (teal) and SBSP (orange) sites in 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, and 2010.
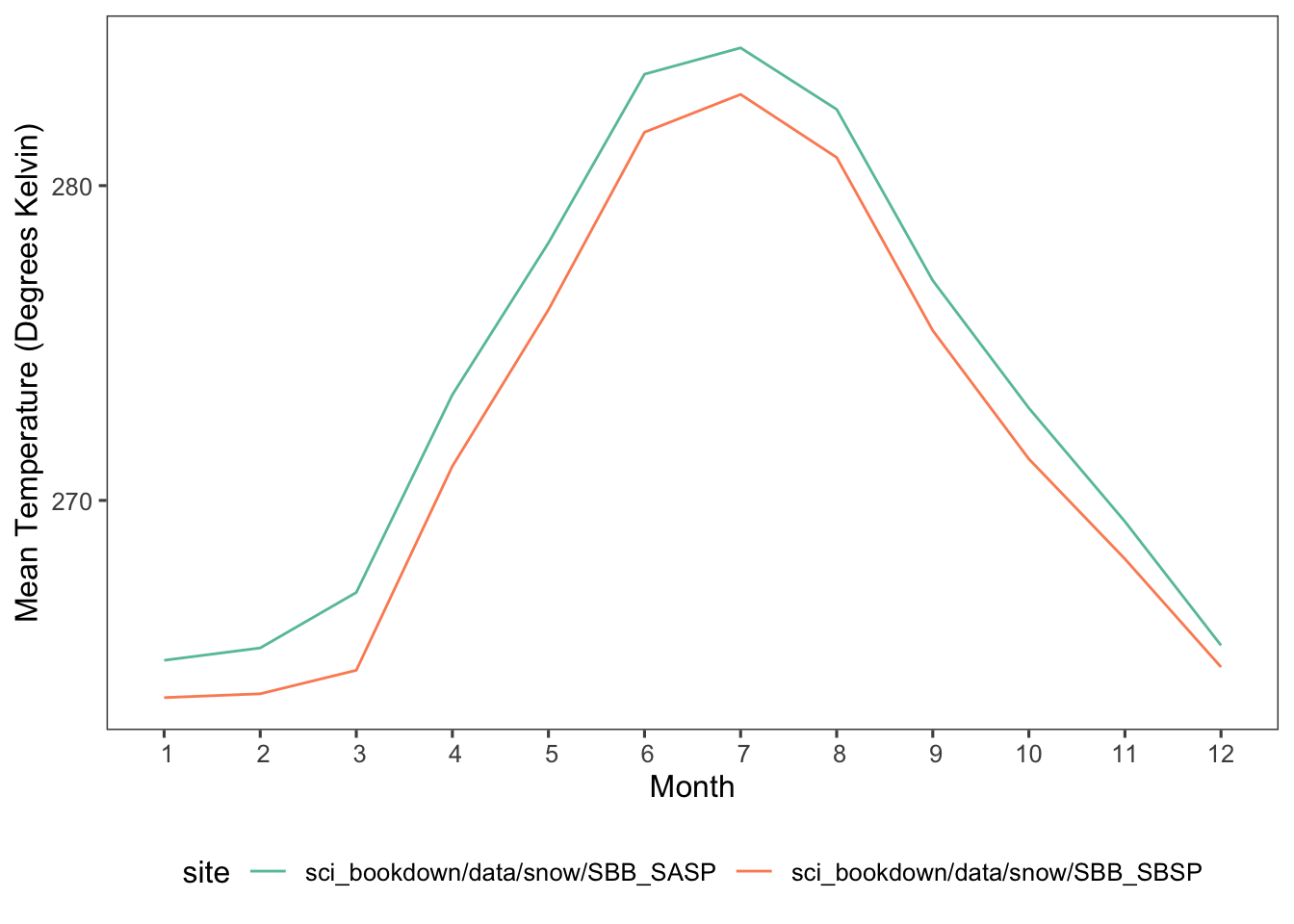
Figure 5.3: Mean monthly temperatures in degrees Kelvin for SASP (teal) and SBSP (orange) sites in 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, and 2010.
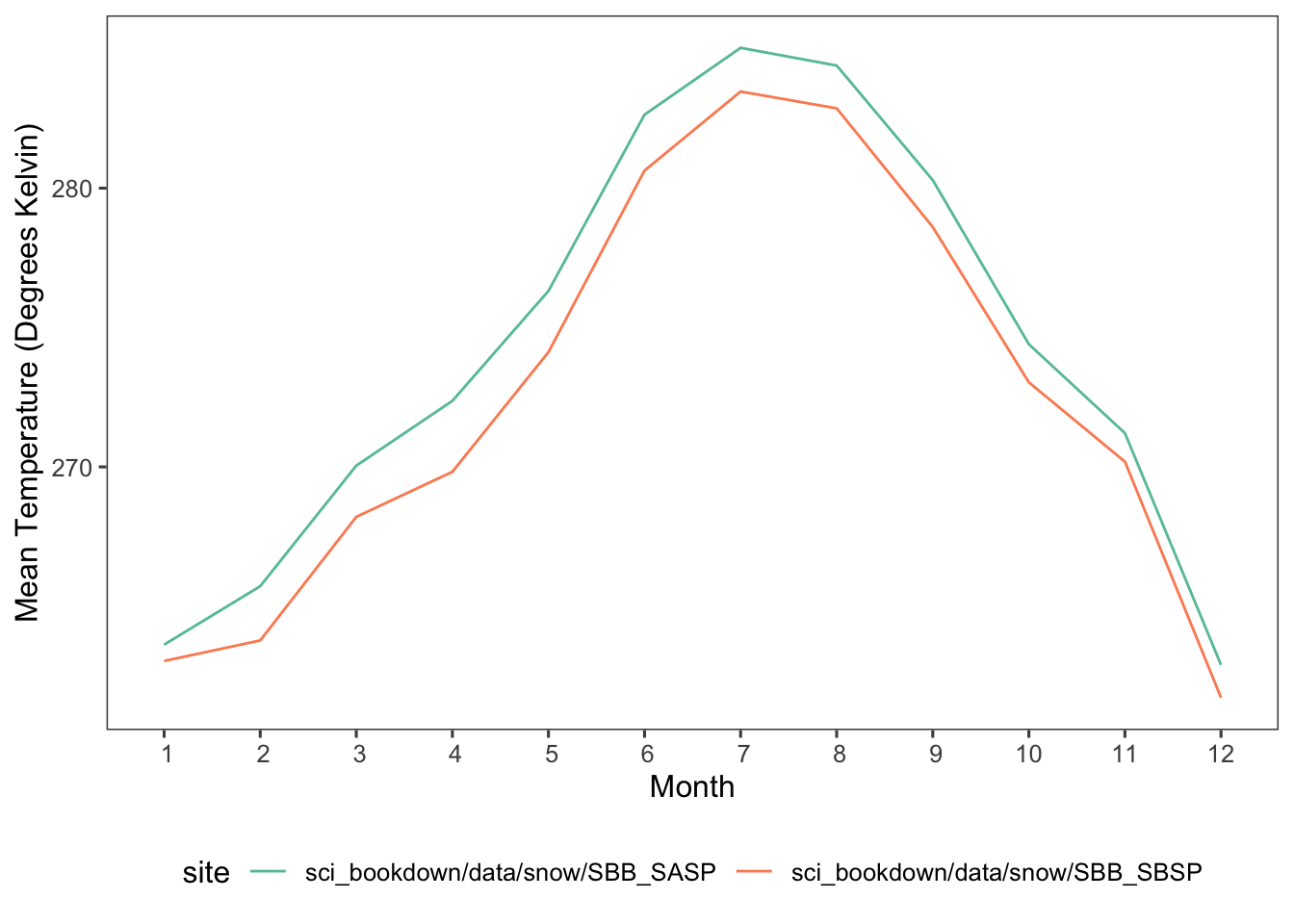
Figure 5.4: Mean monthly temperatures in degrees Kelvin for SASP (teal) and SBSP (orange) sites in 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, and 2010.
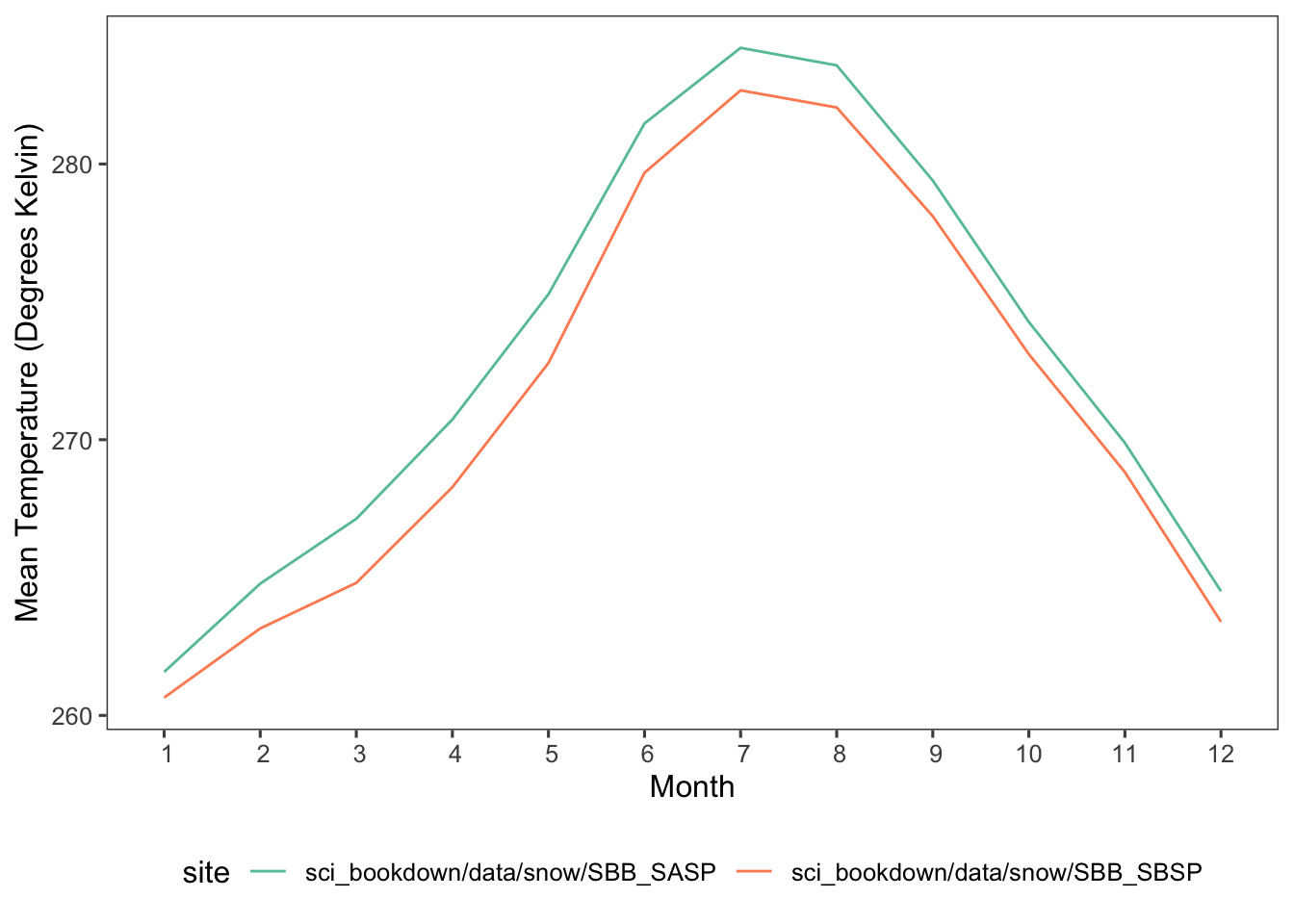
Figure 5.5: Mean monthly temperatures in degrees Kelvin for SASP (teal) and SBSP (orange) sites in 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, and 2010.
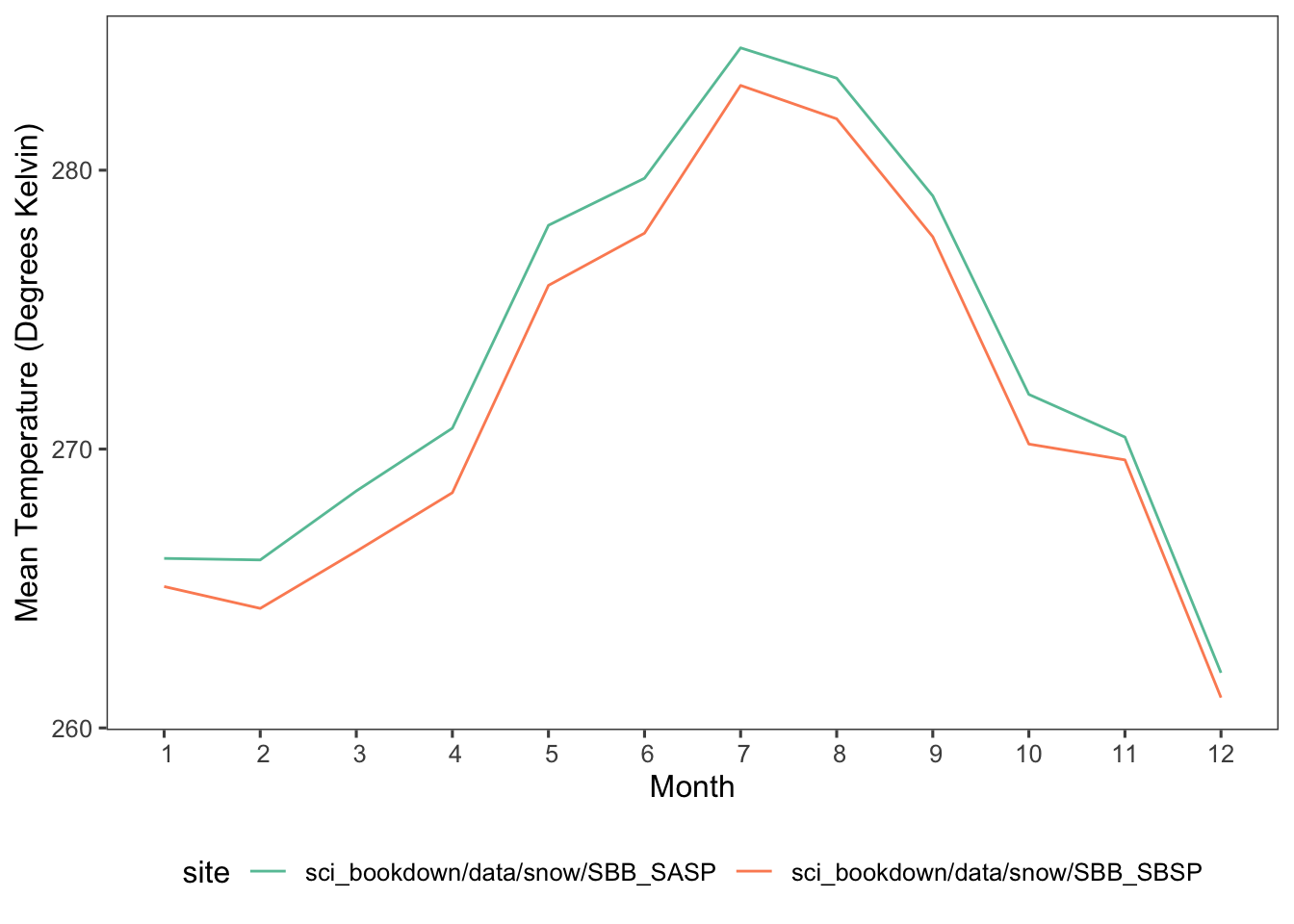
Figure 5.6: Mean monthly temperatures in degrees Kelvin for SASP (teal) and SBSP (orange) sites in 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, and 2010.
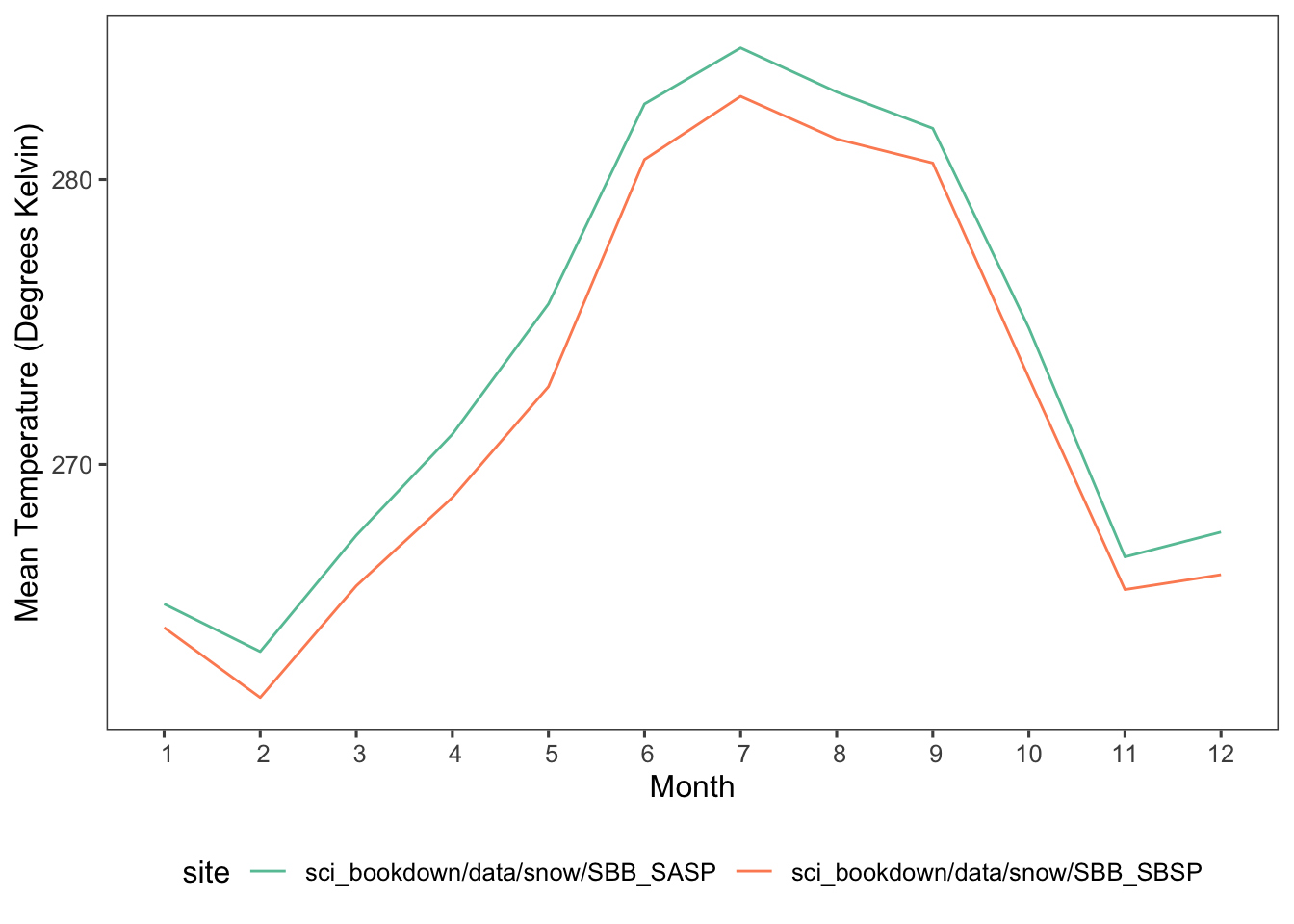
Figure 5.7: Mean monthly temperatures in degrees Kelvin for SASP (teal) and SBSP (orange) sites in 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, and 2010.
5.7 Make a plot of average daily precipitation by day of year (averaged across all available years)
precip_daily <- alldata2 %>%
mutate(date = make_date(year, month, day),
day_no = yday(date)) %>%
group_by(day_no) %>%
summarize(mean_precip = mean(`precip`*86400, na.rm=T))
ggplot(precip_daily, aes(x=day_no, y=mean_precip)) +
geom_line() +
xlab("Day of Year") + ylab("Mean Precipitation (mm/day)") +
ggthemes::theme_few() +
scale_color_brewer(palette = "Set2") +
scale_y_continuous(breaks = pretty(c(0,14), n = 7)) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = pretty(c(1,365), n = 8))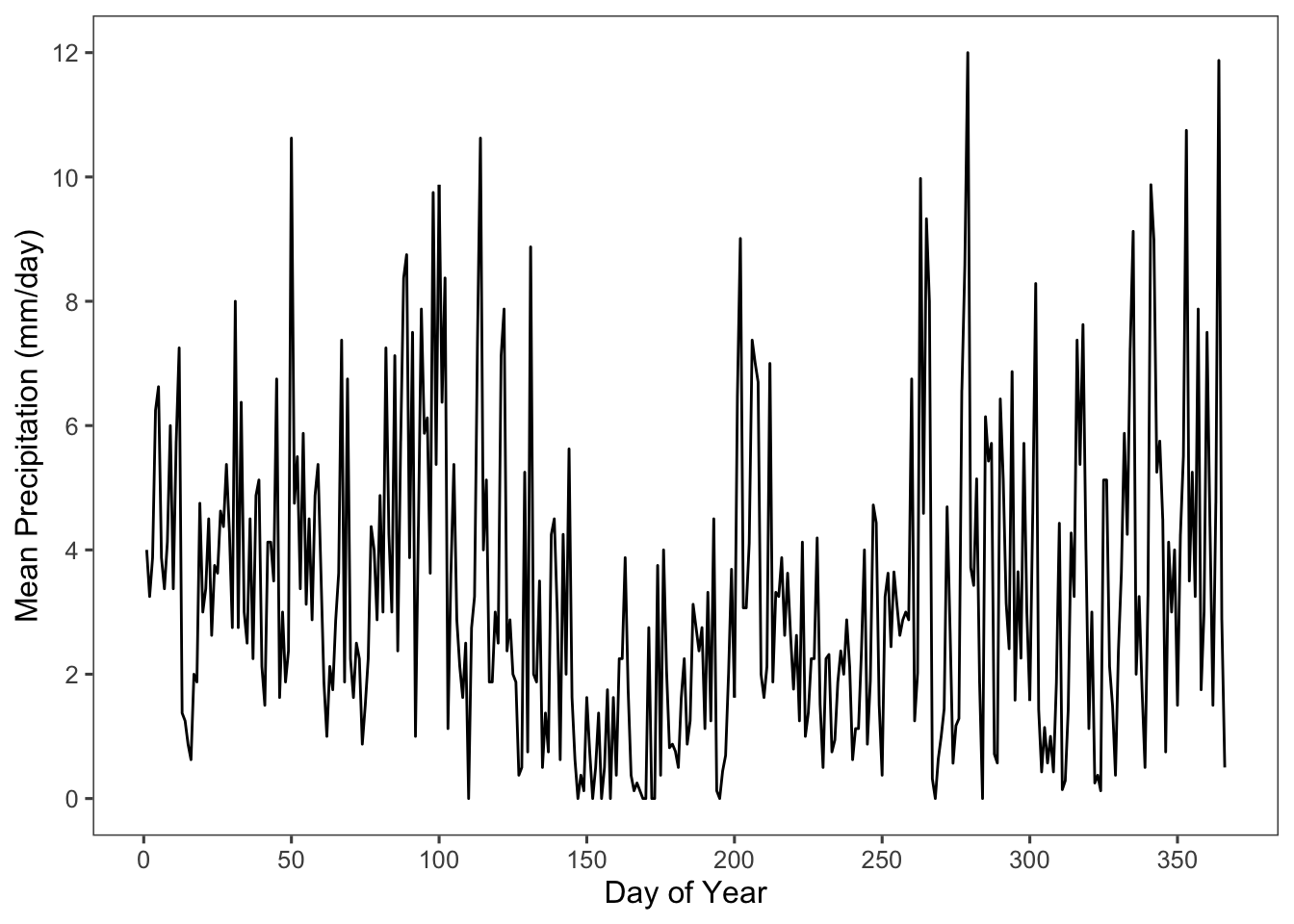
Figure 5.8: Mean daily precipitation by day of year, averaged from 2003 to 2012.